ARM BKPT指令和半主机(Semi-hosting)模式实现的研究
今日排虫遇到了BKPT指令, 研究发现它和调试器有很大关系, 简单研究研究.
起因
今日排虫遇到了这个BKPT指令
调试点对点无线通讯 然而只有一台J-Link调试器 所以需要在两台目标板间不断切换
插拔插拔
问题突然就来了 一板子跑着跑着就死掉了
于是重新接上调试器 想查看它死在了哪里
发现程序停在了一个曾经下过断点的位置
对应的指令为
1 | BKPT 0x0000 |
经过各种调查研究 发现它和调试器的”Flash breakpoints”功能有关,先给出结论:
J-Link的这个Flash breakpoints功能是通过BKPT指令实现的, 使能一个Flash断点, 调试器就在对应的目标程序地址的指令改写成BKPT, 踩到该指令后程序停止运行, 用户继续运行时将指令还原, 恢复现场继续运行.
这里记录一下探索过程和BKPT相关知识
BKPT啥玩意儿
查看ARM汇编参考手册得到以下信息:
1 | BKPT |
总之BKPT就是个ARMv5T之后加入的中断指令: 当程序运行到这个指令所在的地址时 处理器进入Debug状态 调试工具可以利用这个指令调查此时的系统情况.
了解到指令和调试器的断点相关之后 顺着设置面板找到了这个”Flash breakpoints”功能:
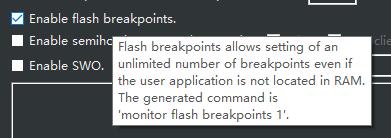
1 | Flash breakpoints allows setting of an unlimited number of breakpoints even if the user application is not located in RAM. The generated command is 'monitor flash breakpoints 1' |
这条指令实现的就是所谓的“软件断点”。
于是J-Link是怎么实现不限数量的断点的呢
https://www.segger.com/products/debug-probes/j-link/technology/flash-breakpoints/
How Does this Work?
A: Basically very simple:
The J-Link software reprograms a sector of the flash to set or clear a breakpoint.
好吧JLink直接写了Flash。
BKPT与Semihosting(半主机模式)
在Cortex-M3的手册中还多了个Note:
1 | ARM does not recommend the use of the BKPT instruction with an immediate value set to 0xAB for any purpose other than Semi-hosting. |
嗯 由此看来Semihosting也是利用这个指令来实现和片子和调试器交互的
这里顺便研究一下半主机模式
什么是半主机
ARM RealView手册里对半主机的介绍:
1 | 8.1.1. 什么是半主机? |
1 | Note |
https://community.nxp.com/message/630895
(todo: )
说起软件断点,那硬件断点是什么呢
如CM3内核中,arm_cortexm3_processor_trm_100165_0201_00_en.pdf中对DWT有描述,就是可以追踪PC地址和数据地址的访问的寄存器,用它实现的断点就是硬件断点
类似的还有FPB寄存器,可以对闪存地址重映射实现断点,这个应该也算硬件断点。
md懒癌 先丢出来吧..